Sector-Specific Benefits
Communications & Internet:
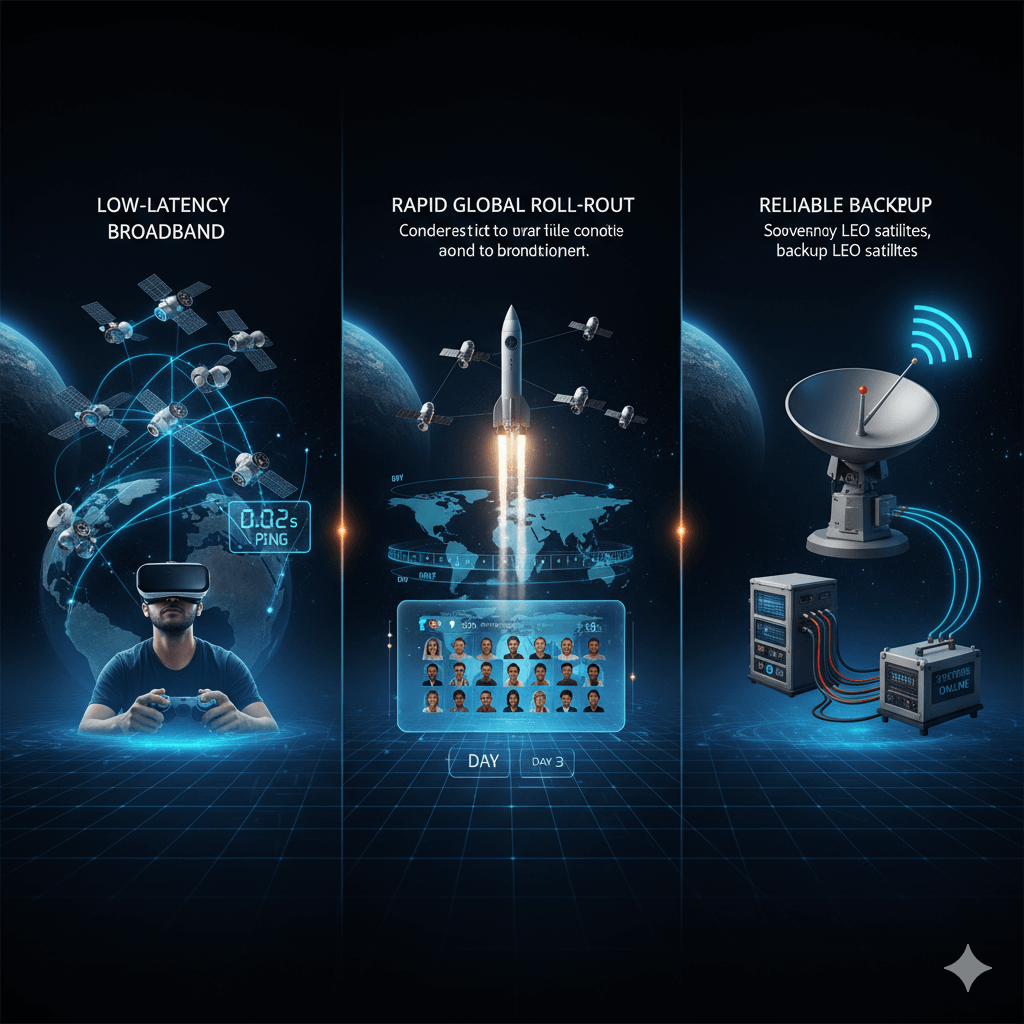
- Low-latency broadband: With LEO satellites, interactive applications experience minimal delay, making real-time communication and gaming smoother.
- Rapid Global Roll-Out: Services can be deployed within hours or days, depending on operational needs. The satellites can deliver the same content to many users at once, saving time and bandwidth.
- Reliable Backup: A reliable backup provides consistent support and maintains essential services.
Earth Observation & Remote Sensing
- Disaster monitoring with revisit intervals in minutes.
- Faster insight delivery with automated analytics.
- Persistent weather watch with GEO satellites.
Navigation & Timing (GNSS)
- Precise synchronisation for networks and finance.
- Accurate positioning for logistics and emergency response.
Science & Research
- Time-series monitoring of atmospheric and space phenomena.
- Rapid-response missions via small satellites.
Defence & Security
- Near-real-time intelligence and surveillance.
- Tactical communications without reliance on local infrastructure.
Internet of Things (IoT)
- Real-time telemetry for moving assets (LEO).
- Efficient periodic updates for static sensors (MEO/GEO).
Practical Examples:

- Disaster response: Satellite imagery reduces reconnaissance-to-action from days to minutes.
- Maritime monitoring: AIS tracking enables near-real-time anomaly detection.
- Content delivery: Global broadcasts achieve uniform latency for live events.
- Financial systems: GNSS-based timestamps enable fast, synchronised trading worldwide.
Implementation Considerations:
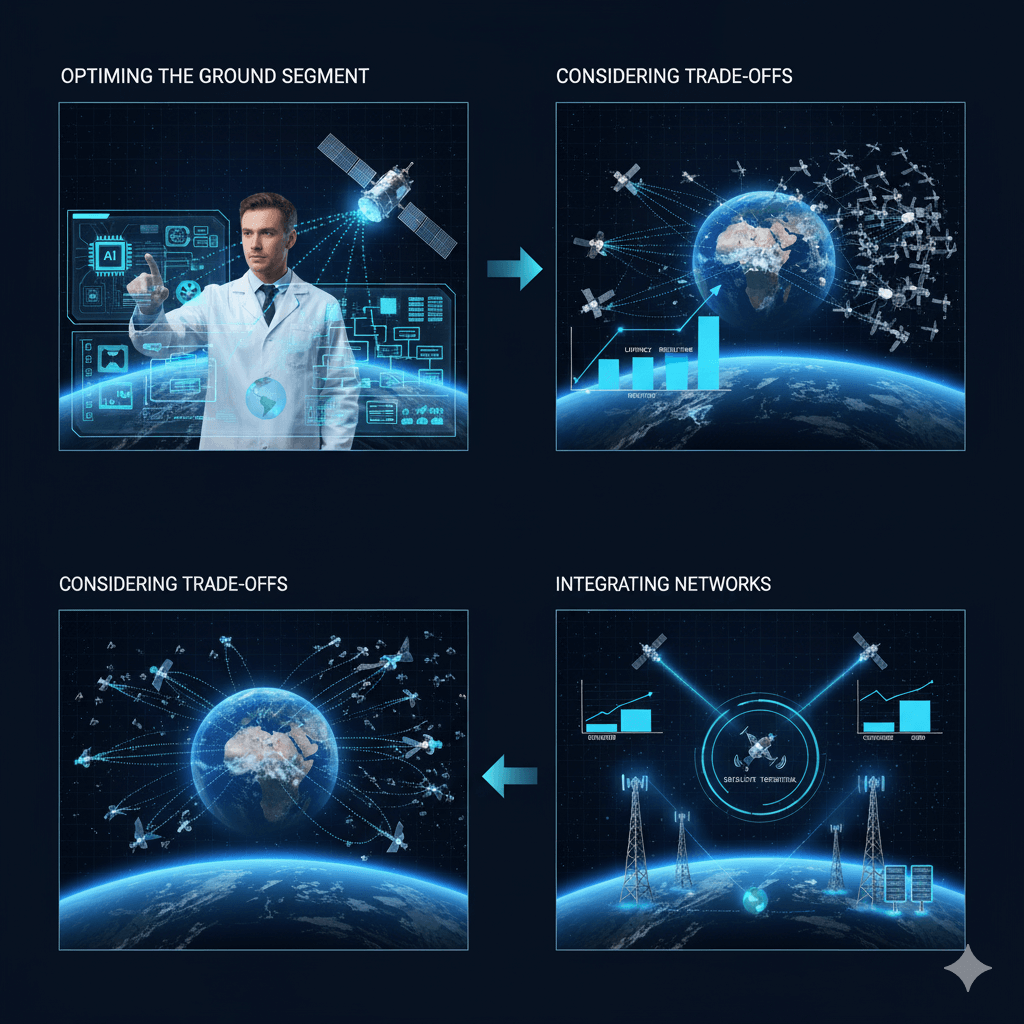
- Optimising the ground segment: By using edge computing and AI pipelines, processing delays can be minimised.
- Scaling constellations: Adding more satellites improves latency and revisit times.
- Considering trade-offs: Achieving higher revisit rates often comes at the cost of lower resolution.
- Integrating networks: Combining satellite and terrestrial systems provides the best balance of coverage and speed.
Quick Reference Metrics:
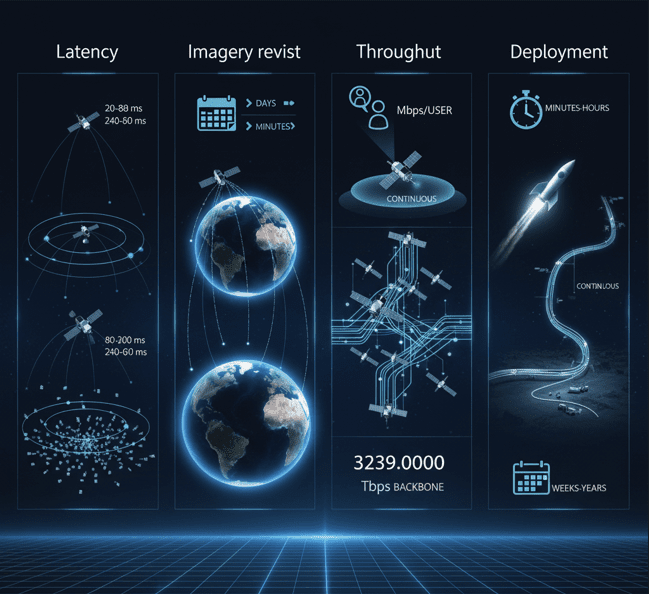
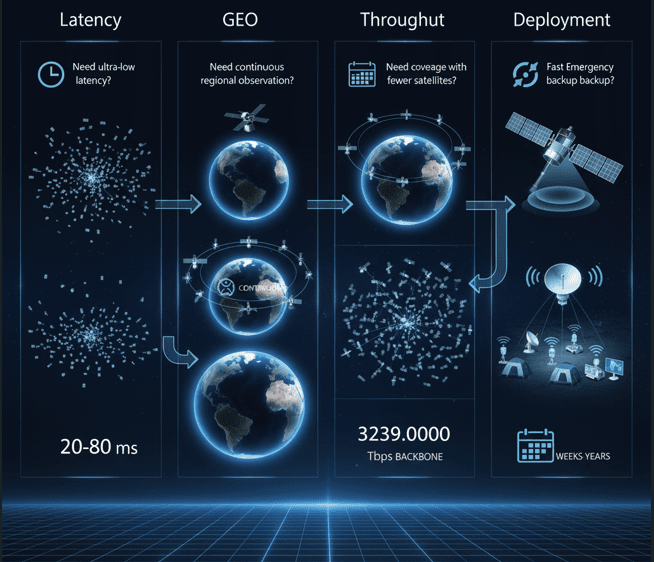
- Latency: LEO 20–80 ms | MEO 80–200 ms | GEO 240–600 ms
- Imagery revisit: LEO days → minutes (with constellations), GEO continuous
- Throughput: Tens–hundreds Mbps/user; Tbps backbone
- Deployment: Minutes–hours (satellite) vs weeks–years (fibre)
Decision-Maker’s Checklist:
- Need ultra-low latency? → LEO
- Need continuous regional observation? → GEO
- Need global coverage with fewer satellites? → MEO/GEO
- Need frequent updates? → LEO constellation
- Need large-scale broadcast? → GEO / HTS
- Need fast emergency backup? → Satellite terminals
Persuasive Talking Points:
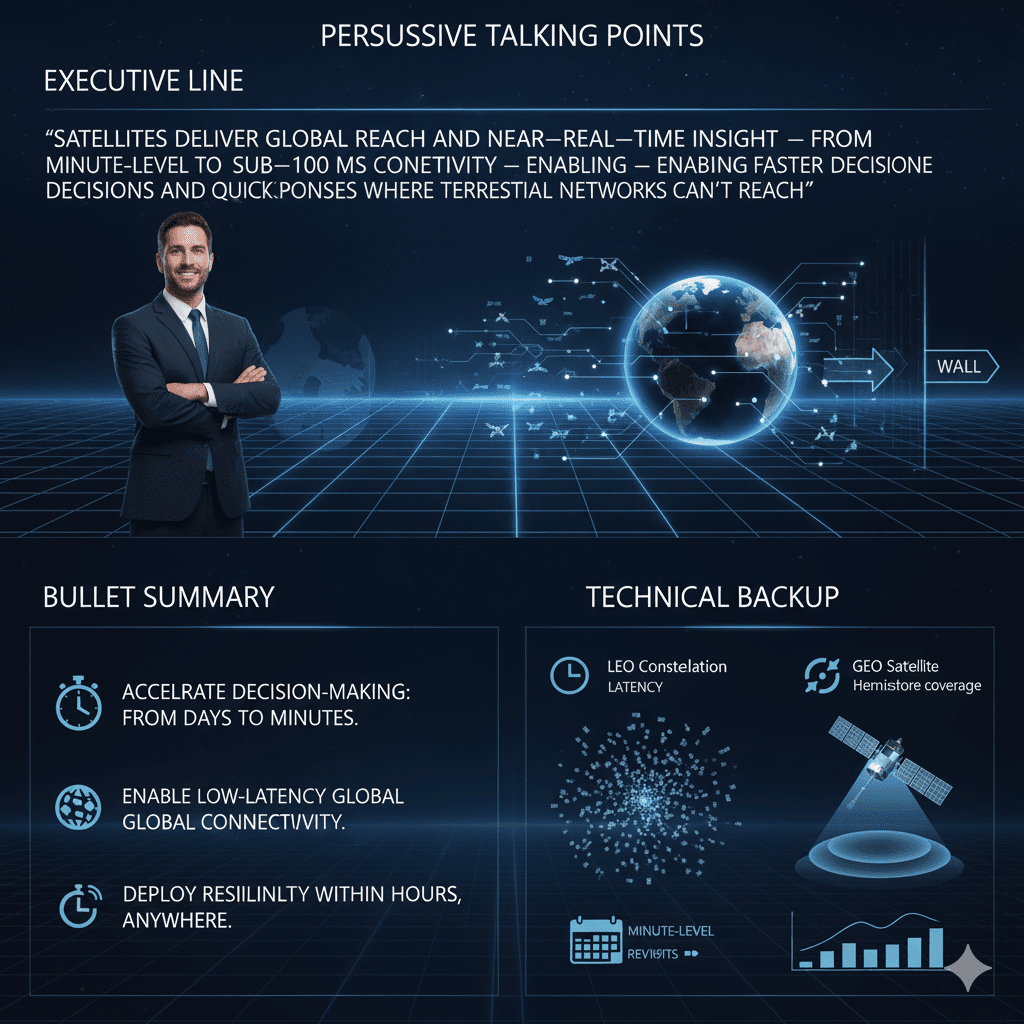
1 Executive line: “Satellites deliver global reach and near-real-time insight — from minute-level imagery revisits to sub-100 ms connectivity — enabling faster decisions and quicker responses where terrestrial networks can’t reach.”
2 Bullet summary:
- Accelerate decision-making: from days to minutes.
- Enable low-latency global connectivity.
- Deploy resiliently within hours, anywhere.
- Technical backup: LEO constellations: 20–80 ms latency, minute-level revisits. GEO: continuous hemisphere coverage
Roadmap for Speed-Focused Programmes:
- Define time SLAs (e.g. images delivered <60 minutes, latency <80 ms).
- Select orbital regime to match SLA.
- Automate processing with edge/cloud analytics.
- Build resilience with failover testing.
- Measure and iterate with timestamped workflows.

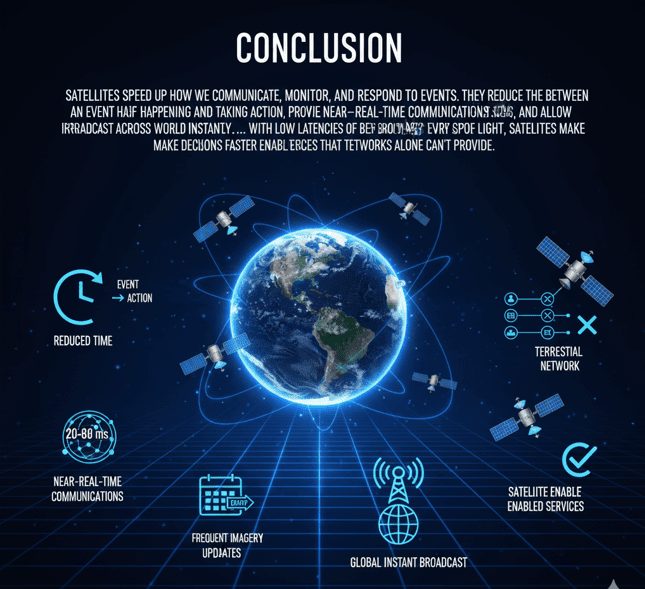
Conclusion: