The World of the Sky Stars
What are Stars?
Stars are massive, luminous spheres of plasma held together by their own gravity. They are born within the dense regions of molecular clouds—vast areas of space containing gas and dust. These clouds collapse under their own gravity, forming dense cores that eventually ignite nuclear fusion in their centre, giving birth to a star.

The energy produced by stars comes from nuclear fusion, primarily the fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium. This process releases immense amounts of energy in the form of light and heat, which radiate outward into space. Our Sun is a typical star, providing the Earth with the energy needed to sustain life.
The Life Cycle of a Star
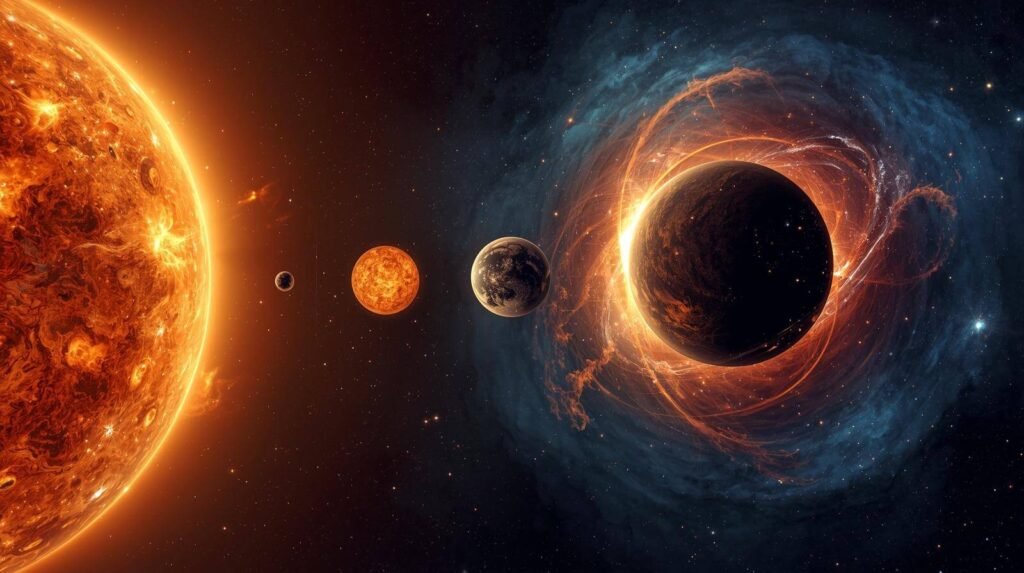

Stars, like living organisms, have a life cycle. The life cycle of a star depends on its mass. Here’s a simplified overview:
- Nebula: Stars are born in nebulae, vast clouds of gas and dust.
- Protostar: Gravity pulls the gas and dust together, forming a protostar.
- Main Sequence Star: Nuclear fusion ignites in the core, and the star enters the main sequence phase, where it spends most of its life. Our Sun is currently in this phase.
- Red Giant: As a star exhausts its hydrogen fuel, it expands into a red giant. The core contracts and heats up, causing the outer layers to expand significantly.
- Final Stages: The final stages depend on the star’s mass:
- Small to Medium Stars: Become white dwarfs, eventually cooling down to become black dwarfs.
- Massive Stars: Explode as supernovae, leaving behind either neutron stars or black holes.
Interesting Star Facts
| 1- The closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri, about 4.24 light-years away. 2- Stars twinkle because of the Earth’s atmosphere, which distorts the light as it passes through. 3- The largest known star is UY Scuti, a hypergiant with a radius about 1,700 times that of the Sun. 4- Stars come in various colours, depending on their surface temperature. Blue stars are the hottest, while red stars are the coolest. |
| 1- The closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri, about 4.24 light-years away. 2- Stars twinkle because of the Earth’s atmosphere, which distorts the light as it passes through. 3- The largest known star is UY Scuti, a hypergiant with a radius about 1,700 times that of the Sun. 4- Stars come in various colours, depending on their surface temperature. Blue stars are the hottest, while red stars are the coolest. 5- Constellations are patterns of stars in the night sky, often named after mythological figures or animals. There are 88 officially recognized constellations. 6- Neutron stars are incredibly dense remnants of supernovae. A teaspoonful of neutron star material would weigh billions of tons on Earth. 7- Black holes are regions of spacetime with such strong gravity that nothing, not even light, can escape from them. 8- Stars recycle matter! Supernova explosions spread heavy elements created in the star’s core into space, enriching the interstellar medium and providing the building blocks for new stars and planets |
Stars in Culture
Stars have held immense cultural and spiritual significance throughout human history. Many ancient civilizations used stars for navigation, agriculture, and religious practices.
- Ancient Egyptians associated stars with gods and believed they represented the souls of the dead.
- Greek mythology is filled with stories of constellations, often depicting heroes and mythical creatures.
- Indigenous cultures around the world have their own unique stories and interpretations of the stars, using them for storytelling, timekeeping, and guidance.

Today, stars continue to inspire awe and wonder, driving scientific exploration and artistic expression. Whether through astronomy, astrology, or simply gazing at the night sky, the stars connect us to the vastness of the universe and our place within it.
Summary
This article explored the fascinating world of stars, from their fiery birth in nebulae to their eventual demise as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. We discovered interesting facts about stars, such as their varying colours and sizes, and their significant role in different cultures throughout history. The stars continue to captivate our imaginations and drive our understanding of the universe.





